HEMATOLOGY
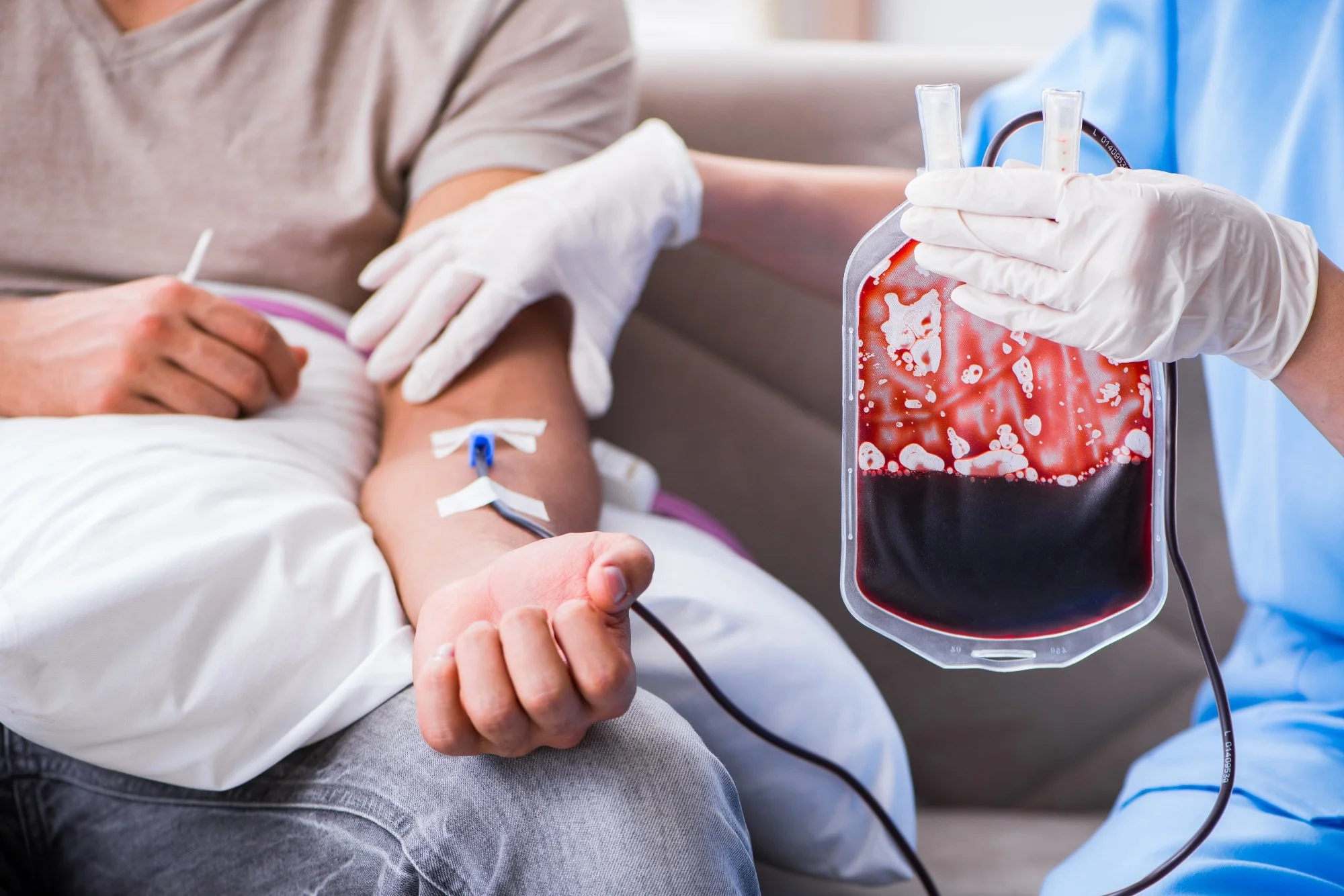
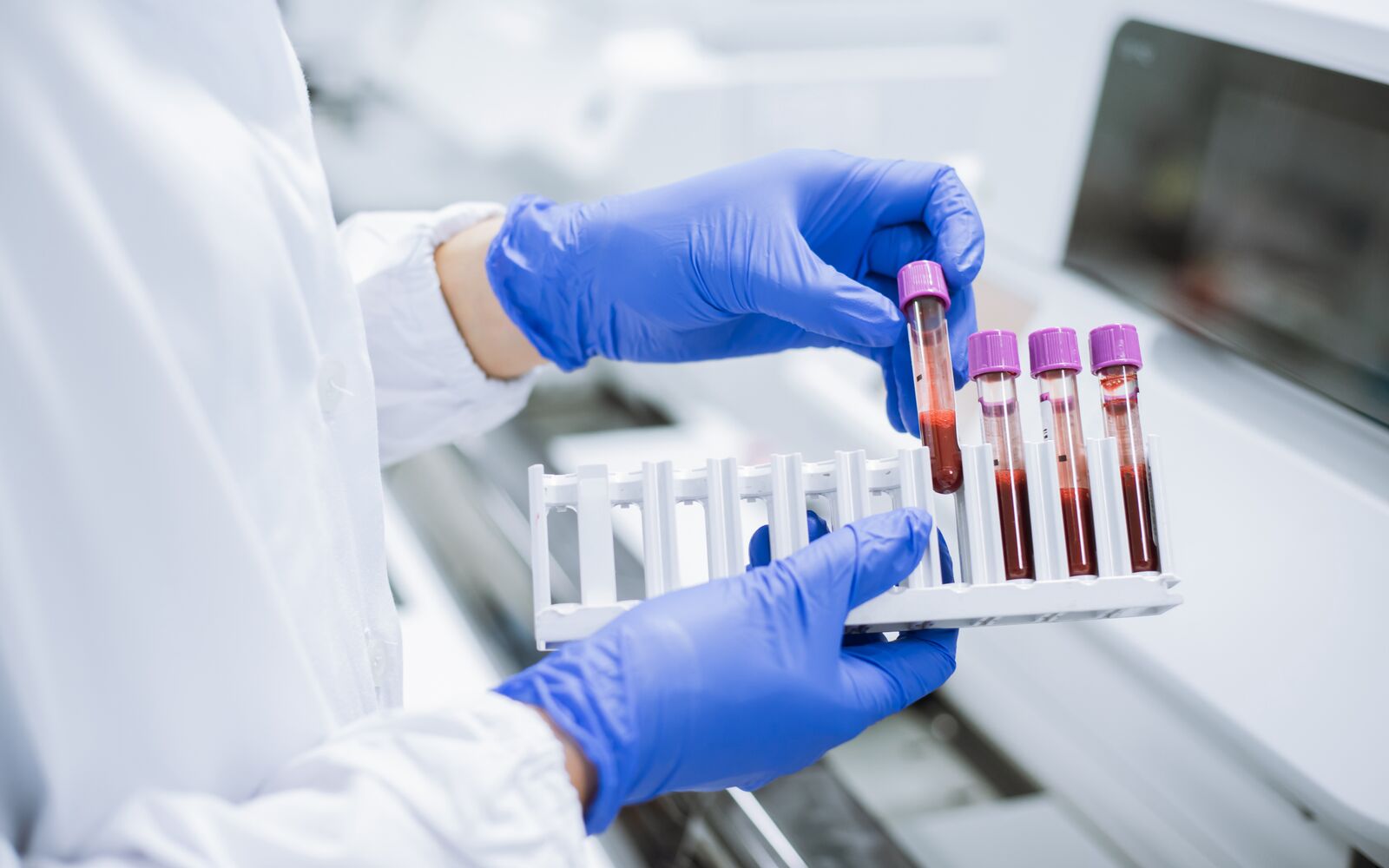
Hematology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the study of blood, blood-forming tissues, and disorders related to them. This field encompasses a wide range of topics, including the structure and function of blood cells, blood clotting mechanisms, bone marrow function, and the diagnosis and treatment of blood disorders and cancers.
Here are some key aspects of hematology:
Blood Components: Hematologists study the different components of blood, including red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets. They examine their formation, functions, and interactions to understand normal blood physiology.
Blood Disorders: Hematology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of various blood disorders, including anemia (low red blood cell count), leukopenia (low white blood cell count), thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), and others.
Hematologic Cancers: Hematologists are involved in the management of blood cancers, such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma. They play a crucial role in the diagnosis, staging, and treatment of these malignancies.
Coagulation and Hemostasis: Hematologists study the processes of blood clotting and hemostasis. They diagnose and treat disorders related to coagulation, such as hemophilia (a bleeding disorder) and thrombosis (excessive clotting).
Bone Marrow Disorders: The bone marrow is responsible for producing blood cells. Hematologists investigate disorders affecting the bone marrow, including myelodysplastic syndromes and myeloproliferative disorders.
Blood Transfusion: Hematologists are involved in the administration of blood transfusions and the management of blood products. They ensure the safe and appropriate use of blood components in various medical conditions.
Hemoglobinopathies: Hematologists address disorders affecting hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen in red blood cells. Examples of hemoglobinopathies include sickle cell disease and thalassemia.
Laboratory Testing: Hematology involves the interpretation of various laboratory tests, such as complete blood counts (CBC), blood smears, and coagulation studies, to assess the health of the blood and identify abnormalities.
Hematologists often work closely with other medical specialists, including oncologists, pathologists, and transfusion medicine specialists, to provide comprehensive care for patients with blood-related conditions. Advances in hematology contribute to improved diagnostic techniques and treatment options for various hematologic disorders.
